White grubs (the larvae of various beetles such as June beetles, Japanese beetles, European Chafers) and Leatherjackets (crane fly larvae) might be tiny, but they can create chaos to your lawn if left unchecked. With their voracious appetite for grass roots, these pests can turn your once lush green lawn into a brown, spongy mess. But fear not, there are effective ways to identify and control these annoying invaders.
Identifying the Culprits
White grubs start small, but they can grow to be 2-4 centimeters long, depending on the species. They typically have white or yellowish bodies with tan or brown heads and six spiny legs.
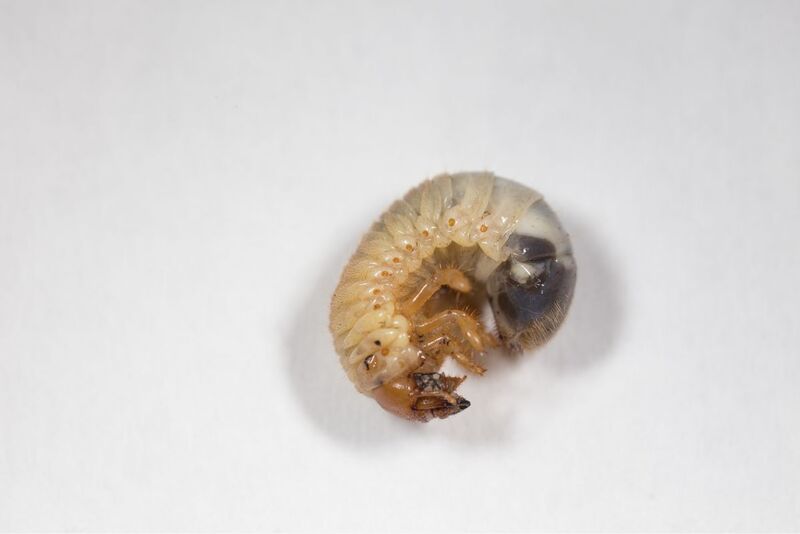

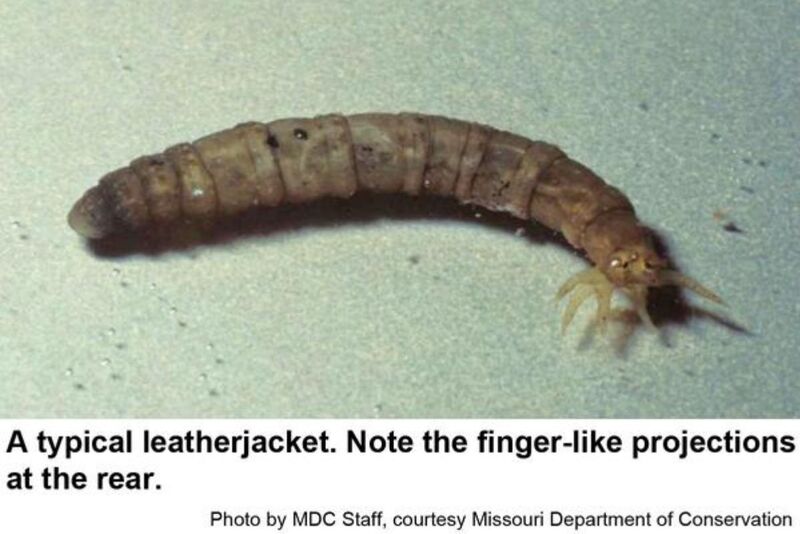
Leatherjacks also start small, finally measuring approximately 3 centimeters in length before pupating. Their coloration ranges from tan to gray with greenish hues, and present a plump appearance, devoid of any discernible legs, like a caterpillar.

Damage - Why do we want to control?
These creatures feed on the roots of grass, causing affected areas to feel soft, spongy, and brown. Signs of their presence include turf that can be easily lifted due to root damage and patches of grass dug up by raccoons or other animals hunting for grubs and leatherjackets. Additionally, starlings and black birds may feast on the damaged turf.
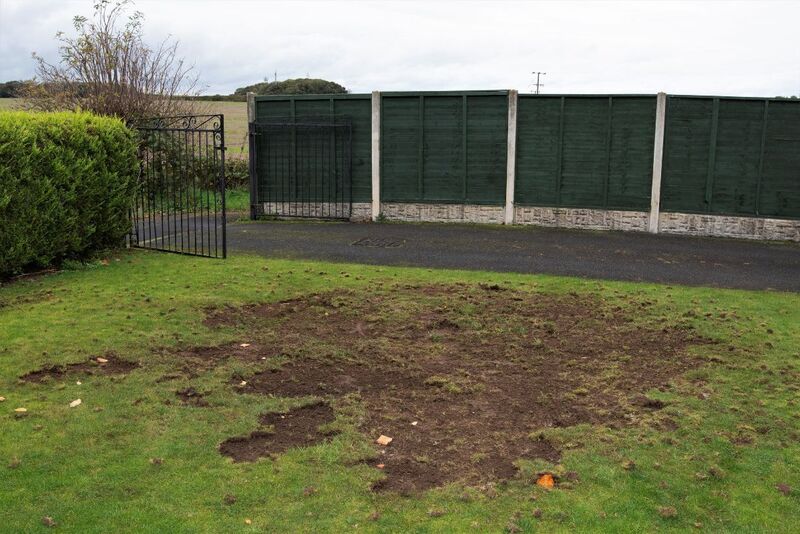

How to Check for an Infestation in your Lawn?
To check if your lawn is infested with white grubs or leatherjackets, simply fold back the turf, and count the number of grubs/larvae exposed. If you find 8-10 grubs/larvae per square foot, it is time to act.
Biological Control with Nematodes
One effective method of controlling white grubs and leatherjackets is using entomopathogenic nematodes. Larvanem (Heterorhabditis bacteriophora) for the white grubs and Capsanem (Steinernema carpocapsae) for the leatherjackets. These microscopic worms enter the pest and release symbiotic bacteria that kill them within days. The offspring of the nematodes then feed on the deceased grubs.

Application and Timing
For control against white grubs, it is best to apply the Larvanem nematodes between late August and early September in regions like Ontario and Quebec, and between mid-July and early August in British Columbia.
Hint: In early spring, white grubs are often targeted with nematode applications. However, applying during the spring poses a challenge for the nematodes as the white grubs have grown over the winter (3rd instar), making it more difficult for the nematodes to effectively penetrate. By treating later in the season, you target the 1st instar white grub, which proves more manageable for nematode control.
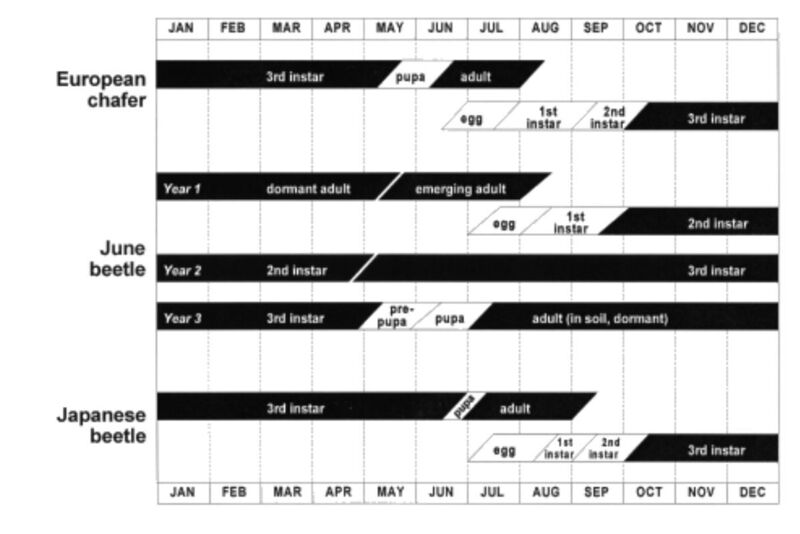
For control against leatherjackets, apply the Capsanem 2-3 weeks after adults become visible on lawns where they are depositing eggs. Typically, this occurs in late July, August, or early fall in most scenarios.
Hint: To maintain a consistent reduction of these pests, annual applications are essential. However, achieving complete eradication may be challenging, as widespread participation from all residents in the neighborhood would be required for effective control
How Many Nematodes Do You Need?
The contents of a 50mill package will treat 2,500sq. ft or 0.06 acres, depending on the level of infestation
The contents of a 500mill package will treat 25,000sq. ft or 0.6 acres, depending on the level of infestation
Ideal Application Conditions:
- Soil Temperature Range: 14-33°C or 57-91°F
- This can be an issue for spring applications, if applying in later in the season (as stated above), you do not have to worry about soil temperature.
- Nematodes are sensitive to Ultraviolet Light (UV). It is best to avoid spraying in direct sunlight. Spray early in the morning, in the late evening or on a cloudy/rainy day.
- Avoid combining with chemicals as nematodes are vulnerable to different pesticides.
- Check our side effects app for more information on compatible products.
Application Instructions:
- Utilize the product promptly or store it between 2-6°C, ensuring usage before the best before date printed on the package.
- When preparing to apply the product, take the packets out of the box and allow them to acclimate to room temperature for 30 minutes.
- After the allotted time, mix the contents with 2 liters of water and let it soak for 5 minutes.
- Avoid leaving the mixture unstirred for more than 30 minutes, as the nematodes may settle at the bottom and suffocate.
- Once the solution is properly mixed, apply it immediately using a Hose End Sprayer with a garden hose or appropriate spray equipment.
- Remove all filters on motorized sprayers, particularly those finer than 0.3mm (50 mesh).
- Use an adequate amount of water to cover the desired treatment area.
- Following nematode application, perform a post-irrigation procedure to wash the nematodes into the root zone.
- Maintain soil moisture for several weeks after application to optimize effectiveness.
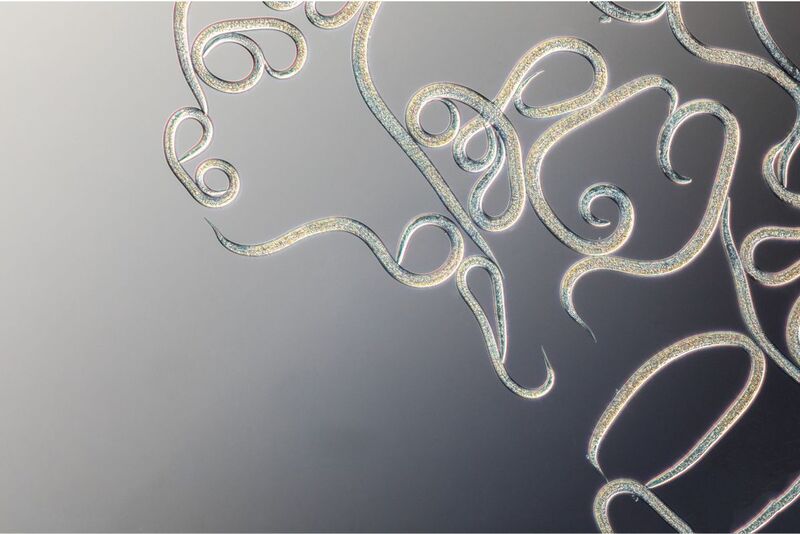

Enhancing Control with Other Natural Products
Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. Galleriae specifically targets beetles without harming other beneficial insects, like pollinators. As white grubs or leatherjackets consume the bacterium, it triggers the bacterium to generate crystal proteins within the pest's body. This process halts the pest's feeding activity on the lawn. Subsequently, the grub undergoes paralysis and eventual demise.
Hint: This product can be applied a week before or after nematode application for enhanced control.
Beauvaria bassiana is a fungus, not a bacterium like Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. Galleriae. This product works by spores germinating and invading the grub, causing its demise. The fungi adhere to the insect's cuticle (outer shell/skin) and enzymatically breaks it down. Once inside the insect's bloodstream (hemolymph), it swiftly colonizes the host's interior, utilizing it for sustenance. As the fungus consumes the grub's nutrients and generates toxins, it transitions to reproductive growth, becoming visible on the outside of the grub. While natural, it may pose a risk to honeybees, beneficial insects, and aquatic life, depending on how you are using this product, so please follow the proper guidelines before applying.
Hint: This product can be applied a week before or after nematode application for enhanced control.
Conclusion
In summary, effective control of lawn pests like white grubs and leatherjackets demands a specifically timed approach. Then utilizing biological control methods like entomopathogenic nematodes and incorporating natural products such as Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. Galleriae and Beauveria bassiana, homeowners can safeguard their lawns. Just make sure you adhere to the proper application procedures, as this will ensure optimal results (getting a high kill rate). With diligence and strategic intervention, homeowners can reclaim their lush green landscapes from the grasp of these troublesome pests.