Aphid control with the parasitic wasp Aphidius ervi


Aphidius ervi is a parasitic wasp species that plays a significant role in biological control of aphids. The natural enemy Aphidius ervi has been widely utilized in various agricultural regions around the world due to its effectiveness. An Aphidius ervi female wasp can parasitize hundreds of aphids within two days. Aphidius ervi is used for the control of the following pests:
- Potato aphid (Macrosiphum euphorbiae)
- Glasshouse potato aphid (Aulacorthum solani)
The parasitic wasp Aphidius ervi is available at Koppert as Ervipar.
Aphidius ervi products
Best conditions for use of Aphidius ervi
The parasitic wasp Aphidius ervi is most effective between 20 and 25°C (68 and 77°F). This natural enemy is not effective at temperatures above 30°C/86°F.
How to use Aphidius ervi
The parasitic wasp Aphidius ervi is available in a bottle (Ervipar).
- Spread the material on rock wool slabs or in Diboxes
- Make sure the material remains dry and is not moved from its introduction site for at least a few days
The dosage of Ervipar depends on climate, crop and aphid density and should always be adjusted to the particular situation. Start introduction preventively soon after planting of the crop. Introduction rates typically range from 0.25-2 per m2/release. Releases should be repeated weekly during the period when aphid infestation is expected. Consult a Koppert advisor or a recognized distributor of Koppert products for advice on the best strategy for your situation.
Behaviour of the parasitic wasp Aphidius ervi


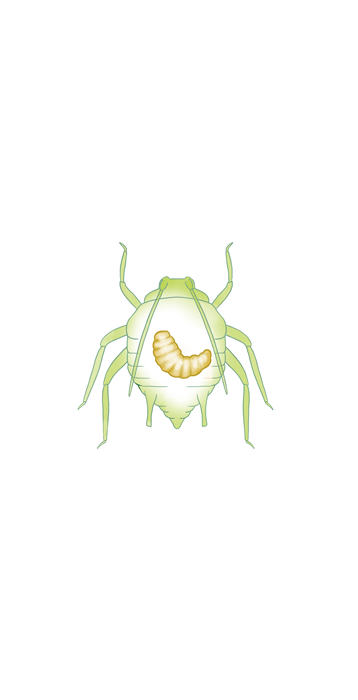
Aphidius ervi exhibits a specialized feeding behavior that makes it an effective biological control agent against aphid pests. Once the female wasp has laid her eggs inside an aphid, the emerging larvae begin their predatory activity by feeding on the aphid's internal tissues. They use their mouthparts to puncture the aphid and consume its bodily fluids, ultimately leading to the host's demise. This parasitic process ensures that Aphidius ervi larvae can eliminate several aphids during their development. The larvae are highly efficient and adaptable, with their feeding rate influenced by the density of the aphid population. In environments where aphids are prevalent, Aphidius ervi can significantly suppress their numbers, making it a valuable agent for integrated pest management. Adult wasps do not feed on aphids but require only nectar and water to sustain themselves.
Life cycle and appearance of Aphidius ervi
Aphidius ervi is a very dark aphid parasitoid. The waist is entirely black, without striping. As it can develop in large aphid species they are generally much larger than Aphidius colemani or Aphidius matricariae. However, if Myzus spp. is their host, they will be of the same size. The parasitization behaviour resembles Aphidius colemani, however, Aphidius ervi is more aggressive and can even pursue the aphid to parasitize. Because of this, the disturbance of aphid colonies can have a serious impact. The aphids can be spread through the crop, and it has been shown that mortality rates among aphids due to disturbance by parasitoids can be very high. A parasitised aphid will turn into a leathery, golden brown mummy.